As the demand for energy continues to increase, the need for alternative sources of power has become more pressing than ever. Hydropower plants, also known as hydroelectric plants, are one such renewable energy source that has been gaining popularity in recent years. In this section, we will provide a comprehensive overview of hydropower plants, explaining what they are and how they positively shape India’s energy landscape.

- Hydropower plants are renewable energy sources that convert the power of water into electricity.
- India’s first hydropower plant played a significant role in kickstarting the growth of this renewable energy source in the country.
- The different types of hydropower plants include run-of-the-river, reservoir, and pumped storage, each with their unique characteristics and applications.
- Hydropower plants have numerous advantages, such as renewable energy generation, water management, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Potential challenges associated with hydropower plants include environmental impact, resettlement issues, and limited site availability.
What is a Hydropower Plant?
A hydropower plant is a renewable energy facility that generates electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy of falling or flowing water. It is a clean and reliable source of energy that helps meet India’s rising power demands while reducing the country’s carbon footprint. Hydropower plants have been in operation for over a century, and they are now one of the most widely used forms of renewable energy in the world.
Hydropower plants work by using a turbine to convert the potential energy of falling or flowing water into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy then powers a generator, which produces electricity. Hydropower plants can be classified into three main types: run-of-the-river, reservoir, and pumped storage.
| Type of Hydropower Plant | Description |
|---|---|
| Run-of-the-river | A type of hydropower plant that uses the natural flow of a river to generate electricity. It does not require the construction of a dam, and the water is returned to the river after generating electricity. |
| Reservoir | A type of hydropower plant that uses a dam to create a reservoir of water. The water is then released to generate electricity as needed. |
| Pumped storage | A type of hydropower plant that uses excess electricity from other sources to pump water from a lower reservoir to a higher reservoir. The water is then released to generate electricity when demand is high. |
Each type of hydropower plant has its unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on the location, resources, and energy needs. Run-of-the-river plants are ideal for areas with a natural flow of water, while reservoir plants are suitable for areas with limited water resources. Pumped storage plants are useful for balancing the grid and meeting peak power demands.

There are three main types of hydropower plants: run-of-the-river, reservoir, and pumped storage. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications.
Run-of-the-River Hydropower Plants
Run-of-the-river hydropower plants generate electricity by using the natural flow of the river. They do not require a large reservoir to store water. Instead, the water is diverted from the river and passes through a turbine, which drives a generator to produce electricity.
Run-of-the-river hydropower plants are best suited for areas with a consistent water supply and a significant elevation difference between the intake and outflow. They are environmentally friendly compared to other types of hydropower plants due to their minimal impact on the river’s natural flow.
Reservoir Hydropower Plants
Reservoir hydropower plants store water in a dammed reservoir, and the water is released to generate electricity as and when required. The water flows through a penstock, which drives a turbine, generating electricity. This type of hydropower plant is suitable for areas with large water bodies and varying water flows.
Reservoir hydropower plants have the potential to produce large amounts of electricity consistently. However, they can have significant environmental impacts due to the displacement of communities and the alteration of natural river flows.
Pumped Storage Hydropower Plants
Pumped storage hydropower plants act as both energy consumers and producers. During low-demand periods, they pump water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir. During high-demand periods, water is released from the upper reservoir, flowing through a turbine and generating electricity. This type of hydropower plant is suitable for balancing the electricity grid’s demand and supply.
Pumped storage hydropower plants have the capability to respond quickly to the changing demand for electricity. They can also operate as a backup power source during peak demand periods. However, they require large amounts of energy to pump water from the lower to the upper reservoir, and their construction can lead to environmental impact.

India’s history with hydropower plants dates back to the early 20th century when the first hydropower plant in the country was commissioned in 1902. The plant was located in Darjeeling, West Bengal, and was known as the Sidrapong hydel power station. With a capacity of 130 kW, it was a significant step in India’s journey towards harnessing the power of water to generate electricity.
The plant’s construction was made possible by the pioneering efforts of the British engineer, R.E.B. Crompton, who recognized the potential of India’s rivers as a source of renewable energy. The Sidrapong plant was built on the Rungeet River, a tributary of the Teesta River, and was used to power street lighting in the nearby town of Darjeeling.
The success of the Sidrapong plant paved the way for the development of numerous other hydropower plants throughout the country. In the years that followed, many more plants were built, including the Koyna dam in Maharashtra, which became the largest hydroelectric project in India when it was commissioned in 1963.

The commissioning of the Sidrapong hydel power station was a momentous occasion for India. At the time, the country was largely dependent on coal-powered plants for electricity generation, which was expensive and environmentally damaging. The Sidrapong plant, on the other hand, provided a clean and cost-effective source of energy that could be harnessed from the country’s vast network of rivers and water bodies.
The success of the Sidrapong plant also inspired the Indian government to increase its investment in hydropower. Today, India has the fifth-largest installed hydropower capacity in the world, with over 50 GW of installed capacity.
The Largest Hydropower Plant in India
India’s largest hydropower plant is the Sardar Sarovar Dam, located on the Narmada River in the state of Gujarat. The dam is a concrete gravity dam, standing at a height of 163 meters and a length of 1.2 kilometers. It has a reservoir capacity of 9.5 billion cubic meters and a gross installed capacity of 1,450 MW.
The Sardar Sarovar Dam was completed in 2017 and has since become a crucial source of electricity for the western region of India. It generates an average of 5,500 million units of electricity annually, which is approximately 16% of Gujarat’s total power generation.
Aside from its energy generation capabilities, the Sardar Sarovar Dam has also contributed significantly to the development of the local community. It has facilitated irrigation for over 14,000 square kilometers of land, which has led to increased agricultural productivity and rural development.
The construction and operation of the Sardar Sarovar Dam have not been without controversy, however. The project has faced criticism from environmentalists and local communities who have raised concerns about the displacement of villagers and damage to the ecosystem. The government has taken several measures to address these issues and ensure that the project is executed in an environmentally sustainable and socially responsible manner.

At its core, a hydropower plant is a complex system consisting of many different components that work together to generate electricity from the force of water. To understand how it all fits together, let’s take a closer look at the key parts of a typical hydropower plant diagram.
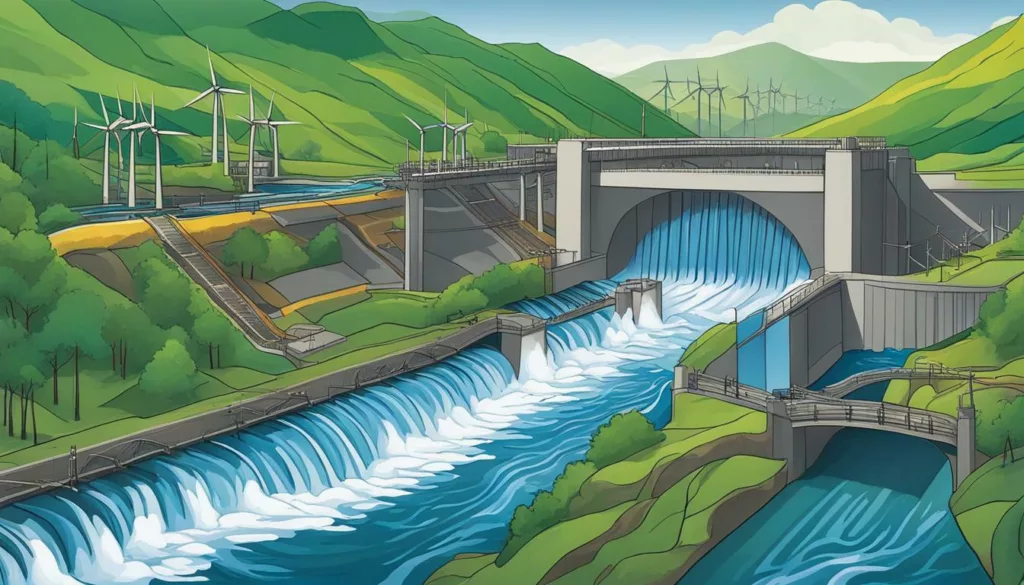

The diagram above shows the main parts of a hydropower plant, from the water source to the power grid. Let’s break it down further:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Water source | The source of water that will be used to generate electricity, such as a river, lake, or reservoir. |
| Intake gate | An opening that allows water to flow into the hydropower plant from the water source. |
| Penstock | A pipe or tunnel that carries water from the intake gate to the turbine. |
| Turbine | A machine that converts the force of water into mechanical energy. |
| Generator | A machine that converts mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy. |
| Transformers | Devices that convert electrical energy from the generator into a higher voltage for transmission to the power grid. |
| Power grid | The network of power lines and substations that distributes electricity to homes, businesses, and other end-users. |
As you can see, there are many moving parts in a hydropower plant that work together to generate clean, renewable energy from the force of water.
Conclusion
The hydropower plant diagram helps us understand the complex workings of this renewable energy source. By harnessing the power of water, we can generate electricity that is clean, reliable, and sustainable, making hydropower plants an essential component of India’s energy landscape.
How Hydropower Plants Work
In order to understand how hydropower plants work, we need to take a closer look at their individual components and how they function together. Hydropower plants generate electricity by harnessing the kinetic energy of falling water.
The process begins with a dam that holds back water, creating a reservoir or pond. The dam’s gates are opened, allowing water to flow through the penstock, which is a tunnel fitted with a turbine. The movement of the water causes the turbine to rotate, which in turn powers a generator that produces electricity.
After passing through the turbine, the water is released into a tailrace, which is a channel or tunnel that leads the water back to the river. The water cycle starts again as the water returns to a lower elevation and flows back to the dam.
Hydropower plants can operate in different ways based on their design and location. For example, run-of-the-river hydropower plants rely on natural water flow without the need for a reservoir, while pumped storage hydropower plants use excess electricity to pump water from a lower to a higher elevation for later use.
Parts of a Hydropower Plant Diagram
Here is a simplified diagram of a typical hydropower plant with labels for each component:
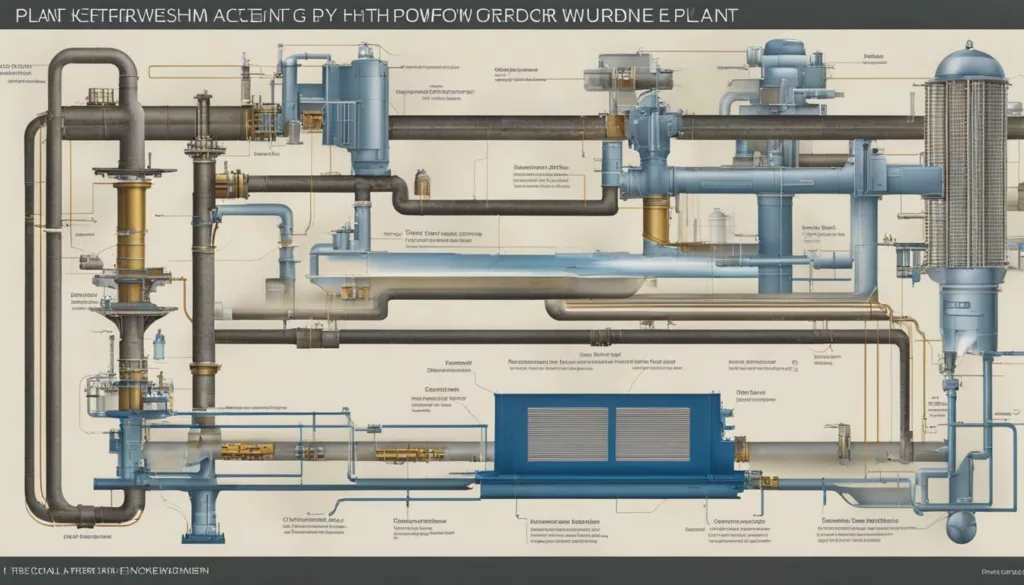
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Dam | A barrier that holds back water, creating a reservoir or pond |
| Intake | An opening through which water flows into the penstock |
| Penstock | A tunnel or pipe that carries water to the turbine |
| Turbine | A machine with blades that are turned by the force of falling water, generating mechanical energy |
| Generator | A machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy |
| Transformers | Devices that increase or decrease the voltage of electricity as needed for transmission |
| Transmission Lines | The network of wires that carries electricity from the generator to consumers |
| Tailrace | A channel or tunnel that leads the water back to the river |
Overall, hydropower plants are a crucial source of renewable energy, providing an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of falling water, hydropower plants have the potential to meet India’s growing energy needs while promoting sustainable development.
Advantages of Hydropower Plants
Hydropower plants offer numerous advantages, making them a crucial source of renewable energy for India. Here are some of the main benefits of hydropower plants:
- Renewable energy generation: Hydropower plants generate electricity using the force of water, a renewable and sustainable resource that will never run out.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Hydropower plants do not produce any greenhouse gas emissions, unlike fossil fuel-based power plants, which contribute to climate change and air pollution.
- Improved water management: Hydropower plants can help manage water resources, preventing flooding and ensuring a reliable water supply for agriculture and other uses.
- Flexible and reliable: Hydropower plants can quickly respond to changes in demand for electricity, making them a flexible and reliable source of power.
- Long lifespan: Hydropower plants can last for up to 100 years, making them a long-term investment in India’s energy infrastructure.
- Low operating costs: Once a hydropower plant is built, its operating costs are relatively low, making it a cost-effective source of electricity.

These advantages make hydropower plants a sustainable and reliable source of electricity that can help meet India’s growing energy demands while mitigating the impact on the environment.
Disadvantages of Hydropower Plants
While hydropower plants have numerous advantages, there are also potential disadvantages and challenges associated with them.
One of the primary concerns is the environmental impact of damming rivers and altering natural water flow patterns. This can lead to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and altered sedimentation patterns in downstream areas, affecting both aquatic and terrestrial systems.
Another issue is the resettlement of local communities that may be displaced due to the construction of hydropower plants. This can lead to economic and social disruptions, as well as cultural loss and psychological stress for those affected.
In addition, the availability of suitable sites for large hydropower plant projects is limited, which can restrict their potential for expansion. Furthermore, the initial capital investment required for construction is often high, making it difficult for smaller or less-developed countries to undertake such projects.
Despite these challenges, there are potential solutions to mitigate their impacts. For example, careful environmental impact assessments and mitigation measures can be taken to minimize the impacts on local ecosystems. Additionally, stakeholder engagement and community involvement can help to address resettlement issues and ensure that the benefits of hydropower plants are shared fairly.

“As with any energy generation system, hydropower plants have their challenges and limitations. However, with proper planning, regulation, and stakeholder engagement, these can be mitigated to ensure that the benefits of this renewable energy source are realized while minimizing its impact on the environment and local communities.”
List of Hydropower Plants in Gujarat
Gujarat is a state in western India that has made remarkable progress in renewable energy generation, including hydropower. Here is a list of hydropower plants in Gujarat:
| Hydropower Plant | Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|
| Kadana Hydroelectric Power Plant | 120 |
| Ukai Dam Hydroelectric Power Station | 300 |
| Dharoi Hydroelectric Power Station | 162 |
| Panam Hydroelectric Power Station | 50 |
| Hydroelectric Power Station at Sardar Sarovar Dam | 1,450 |
These hydropower plants have a combined capacity of over 2000 MW, contributing significantly to Gujarat’s overall electricity generation. The Kadana Hydroelectric Power Plant, located in the Mahisagar district, is the largest hydropower plant in the state with a capacity of 120 MW. The Ukai Dam Hydroelectric Power Station, located in Tapi district, is the second-largest hydropower plant in Gujarat with a capacity of 300 MW.
These hydropower plants have not only helped in meeting the energy demand but also played a significant role in promoting sustainable development. The state government has been keen to promote renewable energy sources and has set ambitious targets for the same. The growth of hydropower plants in Gujarat is a testament to the state’s commitment to clean energy and sustainable development.
Impact of Hydropower Plants on India’s Energy Landscape
Hydropower plants have had a significant impact on India’s energy landscape, playing a crucial role in meeting the nation’s growing energy demands. With the aim of reducing dependence on fossil fuels and promoting sustainable development, hydropower plants have become an important contributor to India’s renewable energy mix.
According to the Central Electricity Authority, hydropower accounts for around 13% of India’s total installed capacity, making it the second-largest source after thermal power. The largest hydropower plant in India, the Sardar Sarovar Dam, has a capacity of 1,450 MW and is located in the western state of Gujarat.
Hydropower plants have several advantages over thermal power plants, including their renewable nature, low operating costs, and efficient energy generation. With increasing concerns over climate change and air pollution, hydropower plants have emerged as a viable alternative to traditional power sources.
In addition to generating clean energy, hydropower plants also offer several ancillary benefits, such as water management and flood control. By regulating water flow and preventing floods, hydropower plants provide vital protection to communities living in flood-prone areas.
Moreover, hydropower plants have played a significant role in rural development and job creation. With several hydropower projects located in remote areas, they provide employment opportunities to local communities and contribute to their economic development.
However, hydropower plants also have their share of challenges, particularly in terms of environmental impact and resettlement issues. While these issues are not unique to hydropower plants, they require careful consideration and mitigation to ensure sustainable and responsible development.

In conclusion, hydropower plants have had a positive impact on India’s energy landscape, providing clean and renewable energy while promoting sustainable development. With technological advancements and policy support, hydropower plants have the potential for further growth, contributing to India’s goal of achieving energy security and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Future Prospects of Hydropower Plants in India
As India continues to strive towards meeting its growing energy demands and reducing its dependence on fossil fuels, the future prospects for hydropower plants in the country are promising. With the development of new technologies and the implementation of supportive policies, the potential for hydropower generation in India is immense.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency, India has the potential to increase its hydropower capacity from the current 45 GW to 148 GW by 2050, enabling it to meet a significant portion of its electricity demand through renewable sources.
One of the key factors driving the growth of hydropower in India is the increasing need for clean energy as the country strives to reduce its carbon footprint. Hydropower plants can play a crucial role in this, providing reliable and efficient electricity generation without emitting greenhouse gases.
Another factor contributing to the growth of hydropower in India is the abundance of suitable locations for plant development, with several major rivers and water reservoirs present throughout the country. Furthermore, the availability of hydropower can help to support the growth of other renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, by providing a stable source of backup power.
Despite the optimistic outlook for hydropower in India, there are also several challenges that need to be addressed. These include regulatory hurdles, opposition from local communities, and the potential environmental impact of plant development. However, with the implementation of effective solutions and greater collaboration between stakeholders, these challenges can be overcome.

In conclusion, the future prospects for hydropower plants in India are bright. With the potential to significantly increase the country’s renewable energy capacity, hydropower can play a crucial role in meeting India’s growing energy demand while also promoting sustainable development. However, it is important that the development of hydropower plants is done in a responsible and sustainable manner, taking into consideration the potential environmental and social impacts and mitigating them accordingly.
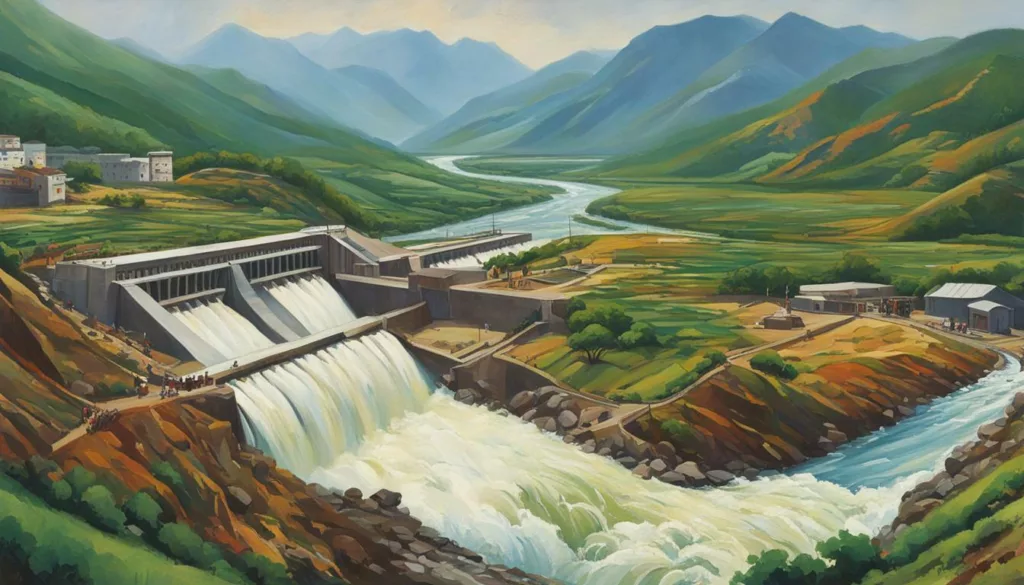
Challenges and Solutions for Hydropower Plants in India
While hydropower plants offer numerous advantages, they also come with various challenges, particularly in the Indian context. One of the primary challenges faced by hydropower plants in India is regulatory hurdles. The process of obtaining necessary clearances and approvals from multiple government bodies can be lengthy and complicated, leading to delays in project implementation.
Another issue is the opposition from local communities, who may be affected by the construction of hydropower plants. The displacement of communities and the loss of their traditional livelihoods can lead to social unrest and further delays in project implementation.
Furthermore, the ecological impact of hydropower plants cannot be overlooked. The construction of dams and reservoirs can result in the loss of natural habitats, while the operation of hydropower plants may harm aquatic ecosystems by altering the water flow and temperature. There may also be an increased risk of landslides and earthquakes in the surrounding areas.
However, these challenges can be addressed through various solutions. To streamline regulatory procedures, the government can establish a single-window clearance system that integrates all necessary clearances and approvals. This can help fast-track projects while ensuring transparency and accountability.
Engaging with local communities is also crucial. Hydropower developers can collaborate with community members to understand their concerns and needs, and offer alternative livelihood options and compensation for the loss of traditional livelihoods. This can help build trust and support for the projects, ultimately leading to their successful implementation.
Regarding ecological concerns, hydropower operators can adopt environmentally friendly practices such as fish ladders and bypass channels to mitigate the impact of dams on aquatic life. They can also implement measures such as afforestation and soil conservation to minimize the risk of landslides and erosion.
Overall, while hydropower plants face challenges in India, it is possible to overcome them through careful planning, community engagement, and sustainable practices. By doing so, hydropower plants can contribute significantly to India’s energy landscape while minimizing adverse impacts on the environment and local communities.

As hydropower plants continue to play a critical role in India’s energy landscape, it is imperative to assess their potential environmental impact. An Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a systematic process that evaluates the potential environmental effects of a proposed project.
Hydropower plants can have a significant impact on the surrounding ecosystem, including aquatic habitats, land use, and water quality. The construction of dams and reservoirs can lead to the displacement of local communities and wildlife, while altered water levels can affect the migration and breeding patterns of fish and other aquatic species. The physical and chemical properties of water can also change due to the release of sediments, nutrients, and pollutants.
However, hydropower plants also have the potential to mitigate their negative environmental impacts through proper planning, design, and operation. For example, the use of run-of-river hydro plants can minimize the need for dam construction and reduce the impact on aquatic ecosystems. Reservoir-based plants can implement sediment traps and water treatment systems to minimize the release of pollutants and maintain water quality.
During the EIA process, potential impacts are identified, and mitigation strategies are developed to minimize environmental effects. The EIA process involves a series of steps, including baseline studies, impact assessment, and management and monitoring plans.

Baseline studies involve collecting data on the existing environmental conditions in the area where the proposed project will be built. This includes information on flora and fauna, soil quality, water resources, and air quality. Impact assessment involves analyzing the potential environmental effects of the project, including identifying any potential impacts on human health, endangered species, or cultural heritage sites.
Management and monitoring plans involve developing strategies for managing any potential negative impacts and monitoring the effectiveness of these strategies over time. Monitoring plans include ongoing assessments of the project’s environmental performance, identifying any changes in environmental conditions, and adjusting the management plans as necessary.
Overall, the EIA process is critical for ensuring that hydropower plants are built and operated in an environmentally responsible manner. By identifying potential impacts and developing mitigation strategies, hydropower plants can help minimize their impact on the environment while still providing a vital source of renewable energy for India’s growing energy needs.
Social and Economic Benefits of Hydropower Plants
Hydropower plants have numerous social and economic benefits, making them a crucial contributor to sustainable development in India. Let’s explore some of these benefits:
Social Benefits
Job creation: Hydropower plants require a skilled workforce to operate and maintain them, leading to the creation of employment opportunities. According to the Central Electricity Authority, the hydropower sector is estimated to create around 2.5 million jobs in India by 2050.
Rural development: Many hydropower plants are located in remote rural areas, providing access to electricity and improving the standard of living for the local communities. This, in turn, leads to rural development and improved economic prospects for the region.
Improved quality of life: Access to electricity through hydropower plants improves the quality of life for people in remote locations, providing access to healthcare, education, and other basic amenities.
Economic Benefits
Reduced dependence on fossil fuels: Hydropower plants are a clean and renewable source of energy, reducing India’s dependence on fossil fuels and the associated costs of importing oil and gas.
Low operating costs: Once a hydropower plant is constructed, the operating costs are relatively low compared to other forms of power generation, making it a cost-effective source of electricity in the long run.
Revenue generation: Hydropower plants contribute significantly to revenue generation for the government, which can be used for infrastructure development and other social welfare programs.

In conclusion, the social and economic benefits of hydropower plants make them a valuable contributor to India’s energy landscape. They not only provide clean and renewable energy but also promote job creation, rural development, and improved quality of life for communities near these plants.
Conclusion
We hope this article has provided you with a clear understanding of hydropower plants, their types, and their impact on India’s energy landscape. Hydropower plants are an essential source of renewable energy for India, contributing significantly to the country’s electricity generation and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Other benefits of hydropower plants include efficient water management, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and job creation in rural areas. However, it is crucial to address the potential environmental and social challenges associated with hydropower plants, including resettlement issues, limited site availability, and opposition from local communities.
To ensure sustainable development, it is vital to conduct comprehensive environmental impact assessments and adopt suitable solutions to minimize the adverse effects of hydropower plants. With the right policies and technological advancements, hydropower plants can continue to play a key role in India’s energy mix while contributing to the country’s economic growth and social development.
Happy Learning
Also, Read,
Stylish Frameless Shower Doors
FAQ
Q: What is a hydropower plant?
A: A hydropower plant is a facility that uses the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. It typically consists of a dam, reservoir, water turbines, and generators.
Q: What are the types of hydropower plants?
A: There are different types of hydropower plants, including run-of-the-river plants, reservoir plants, and pumped storage plants. Run-of-the-river plants harness the natural flow of a river, reservoir plants store water in a dam to generate electricity, and pumped storage plants use excess electricity to pump water into an elevated reservoir and release it back down to generate power when needed.
Q: Which was the first hydropower plant in India?
A: The first hydropower plant in India was the Sidrapong Hydel Power Station, which was commissioned in 1897. It is located in Darjeeling, West Bengal, and has a capacity of 1.5 MW.
Q: What is the largest hydropower plant in India?
A: The largest hydropower plant in India is the Sardar Sarovar Dam, located on the Narmada River in Gujarat. It has a capacity of 1,450 MW and plays a significant role in meeting the electricity needs of the state.
Q: How does a hydropower plant work?
A: A hydropower plant works by harnessing the energy of flowing or falling water. This water is captured in a dam and stored in a reservoir. When released, it flows through turbines, which spin and generate mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then converted into electricity by connected generators.
Q: What are the advantages of hydropower plants?
A: Hydropower plants have several advantages. They provide a renewable and sustainable source of energy, contribute to water resource management by regulating water flow, and produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, they can provide employment opportunities and contribute to rural development.
Q: What are the disadvantages of hydropower plants?
A: While hydropower plants have numerous benefits, they also have some disadvantages. They can cause environmental impacts such as habitat alteration and disruption of fish migration. There may also be challenges related to resettlement and limited availability of suitable sites for construction.
Q: Can you provide a list of hydropower plants in Gujarat?
A: Here is a list of some hydropower plants in Gujarat: – Sardar Sarovar Dam (1,450 MW) – Ukai Dam (1,350 MW) – Dharoi Dam (600 MW) – Kadana Dam (320 MW) – Wanakbori Dam (265 MW)
Q: What is the impact of hydropower plants on India’s energy landscape?
A: Hydropower plants play a crucial role in India’s energy landscape. They contribute to meeting the increasing energy demands, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and promote sustainable development. Hydropower plants also help in stabilizing the grid and providing a reliable electricity supply.
Q: What are the future prospects of hydropower plants in India?
A: The future prospects of hydropower plants in India are promising. With advancements in technology, policy support, and a growing focus on renewable energy, there is potential for the development of additional hydropower capacity. Hydropower plants can continue to play a significant role in India’s energy mix and promote clean and sustainable energy generation.
Q: What are the challenges and solutions for hydropower plants in India?
A: Hydropower plants in India face challenges such as regulatory hurdles, opposition from local communities, and environmental concerns. Solutions to overcome these challenges include transparent and inclusive decision-making processes, community engagement, and adopting best practices for environmental management and mitigation measures.
Q: Why is conducting environmental impact assessments important for hydropower plants?
A: Conducting environmental impact assessments for hydropower plants is important as it helps identify potential environmental impacts and allows for the development of appropriate mitigation measures. This ensures that the plants are built and operated in an environmentally sustainable manner, minimizing adverse effects on ecosystems, water quality, and local communities.
Q: What are the social and economic benefits of hydropower plants?
A: Hydropower plants provide numerous social and economic benefits. They create job opportunities during both the construction and operation phases, contribute to rural development, and improve the quality of life for communities living near these plants. Hydropower plants also support local economies, as they require infrastructure development and maintenance services.



