Steps Involved in the Concreting Process
The concreting process or concrete manufacturing process involves a series of steps that transform the basic ingredients – cement, coarse and fine aggregates, and water – into a classic construction material. Each step is crucial in ensuring that the resulting concrete is of high quality and meets the specific requirements of the construction project.
In this article, we will delve into each step of the concreting process, from batching and mixing to reinforcement and quality control. We will also discuss the environmental impact of the concreting process and explore sustainable practices to minimize its carbon footprint.



What is Concrete?
Concrete is a versatile and durable construction material used in a variety of applications, ranging from buildings and bridges to roads and pavements. It consists of a mixture of cement, water, aggregates, and additives, which can be adjusted to suit specific project requirements and environmental conditions.
The composition of concrete can vary widely depending on the intended use and desired characteristics of the finished product. The amount and type of aggregates used, for example, can affect the strength, density, and porosity of the concrete, while the type and amount of cement can affect its setting time, workability, and finish.
Overall, concrete is highly valued for its strength, durability, and versatility, making it a popular choice for a wide range of construction projects.


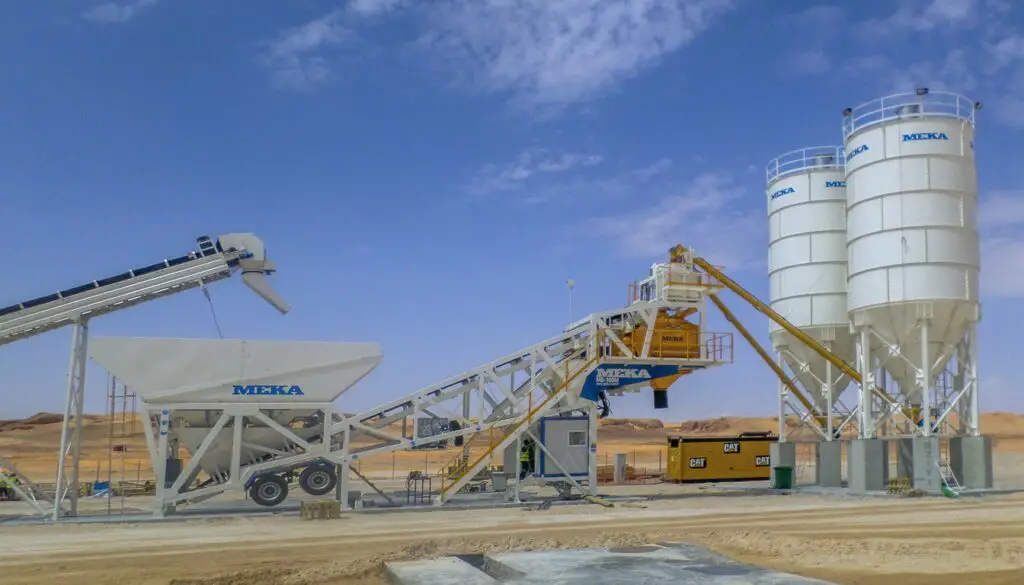
Batching Methods
One of the most critical steps in the concreting manufacturing process is batching, where the ingredients that makeup concrete are measured and combined in specific proportions to create a uniform mixture.
The two primary batching methods used in the concreting process are volume batching and weight batching. Volume batching involves the measurement of ingredients by volume, typically using containers like drums, buckets, or cartons. This method is commonly used for small jobs or less critical applications where high accuracy is not required.
Weight batching, on the other hand, involves measuring ingredients by weight, using scales or balances to ensure the exact amounts are mixed. This method produces more precise and consistent results, making it the preferred option for larger jobs or applications that require a high degree of accuracy.
Note: It is important to note that the batching method used can impact the quality and performance of the final concrete mixture.


Mixing
The second method used in the concreting process is mixing. Mixing is the process of combining the various ingredients of concrete to create a uniform mixture. The two primary materials used in this process are cement and aggregates. The cement, which acts as the binding agent, is mixed with water to form a paste that coats the aggregates.
During the mixing process, it is essential to achieve an even distribution of all materials to ensure adequate strength and durability of the final product. This can typically be accomplished by using a concrete mixer, which comes in various sizes and configurations.
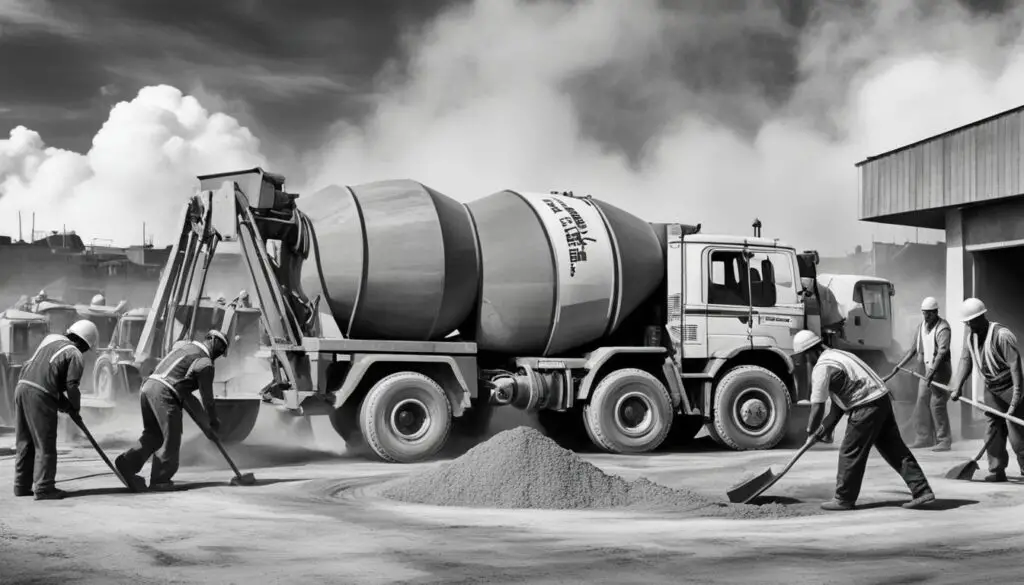


Once the mixing is complete, the resulting concrete mixture must be transported to the construction site as soon as possible to prevent the initial setting process from beginning prematurely. Proper mixing is essential to create a high-quality, long-lasting concrete product that can withstand the rigors of construction and environmental exposure.
Transportation Methods
The third method used in the concreting process is transportation. After the concrete mix is ready, it needs to be transported to the construction site where it will be used to create the desired structure. There are two transportation methods: manual transportation and mechanical transportation.
Manual Transportation:
In small construction projects where concrete is required in amounts that can be carried by hand, manual transportation is the most common method. This method involves the use of wheelbarrows or buckets to carry the concrete mix from the mixer to the construction site. It is a cost-effective and flexible alternative, as it can only be used when and where needed.
Mechanical Transportation:
For projects that require large amounts of concrete, mechanical transportation is the most efficient method. This method involves the use of specialized equipment such as trucks with rotating drums that transport and mix the concrete simultaneously, providing a more uniform and precise mixture. Other mechanical options include pumps and cranes, which can transport concrete to hard-to-reach places on a construction site.
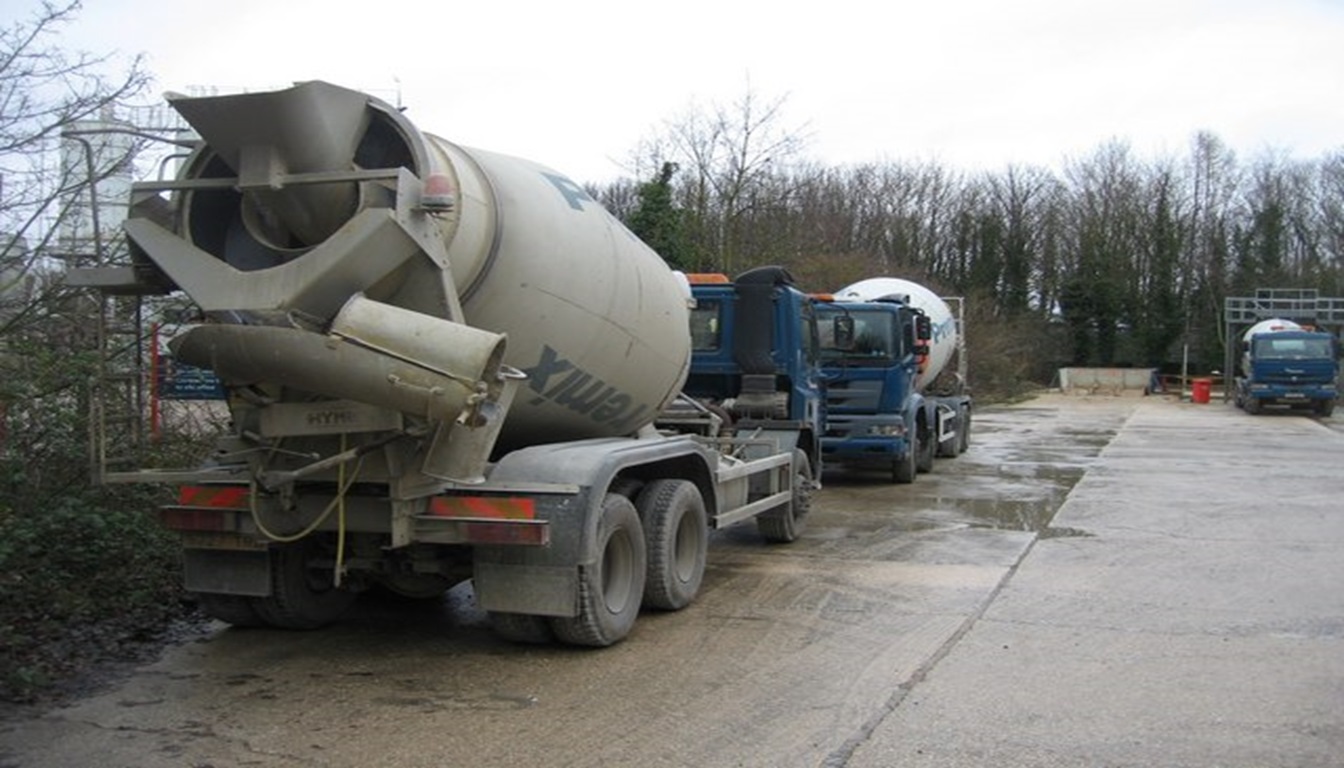


Both manual and mechanical transportation methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and the decision on which to use depends on the project’s requirements, budget, and time constraints.
Compaction
The 4th method used in the concreting process is compaction. Compaction is a critical step in the concrete manufacturing process that helps improve its strength and durability. During the mixing stage, small air pockets can get trapped between the aggregate materials, resulting in concrete that is prone to cracking and is weaker than compacted concrete. To eliminate these air voids, the concrete must be compacted. This process involves using heavy machinery, such as rollers or vibrators, to press the concrete to remove air pockets and create a dense and uniform mixture.
Properly compacting the concrete can increase its strength by up to 20 percent, making it a crucial step in the production process. In addition to improving its strength, compacting the concrete also improves its durability and resistance to wear and tear.


The compaction process should be done immediately after placing the concrete into the formwork before it has a chance to set. The timing and method of compaction can vary depending on the type of concrete being used and the specific construction project. Contractors must ensure that they are using the appropriate equipment and method of compaction to achieve the desired strength and density.
Benefits of Compacted Concrete
Compacting concrete has several benefits, including:
- Improved strength and durability
- Reduced porosity, which helps prevent damage from freeze-thaw cycles and chemical corrosion
- Improved resistance to wear and tear
- Reduced permeability, which minimizes water penetration and potential water damage
By ensuring that the concrete is properly compacted, contractors can help ensure that the finished structure is strong, durable, and built to last.
Curing
The 5th method used in the concreting process is curing. After the concrete is placed and consolidated, it enters the curing process, which is crucial for achieving maximum strength and durability. The curing process involves maintaining the necessary moisture and temperature conditions for the concrete to properly hydrate and set.
The concrete curing process typically lasts for 28 days, during which time the concrete gains strength as a result of the chemical reaction between water and cement. If the concrete is not adequately cured, it may not reach its maximum strength potential and may be more susceptible to cracking and other forms of damage.
One common method of curing is wet curing, which involves keeping the concrete moist by covering it with a layer of water or moist burlap. Another method is to use a curing compound, such as a membrane-forming compound, to retain moisture within the concrete.
It is crucial to ensure that the curing process is carried out properly to promote the structural integrity and longevity of the concrete.
Did you know? Proper concrete curing also helps to prevent shrinkage and cracking.


“Properly curing concrete is critical for reinforcing its strength and durability, helping to ensure that it can withstand the test of time.”
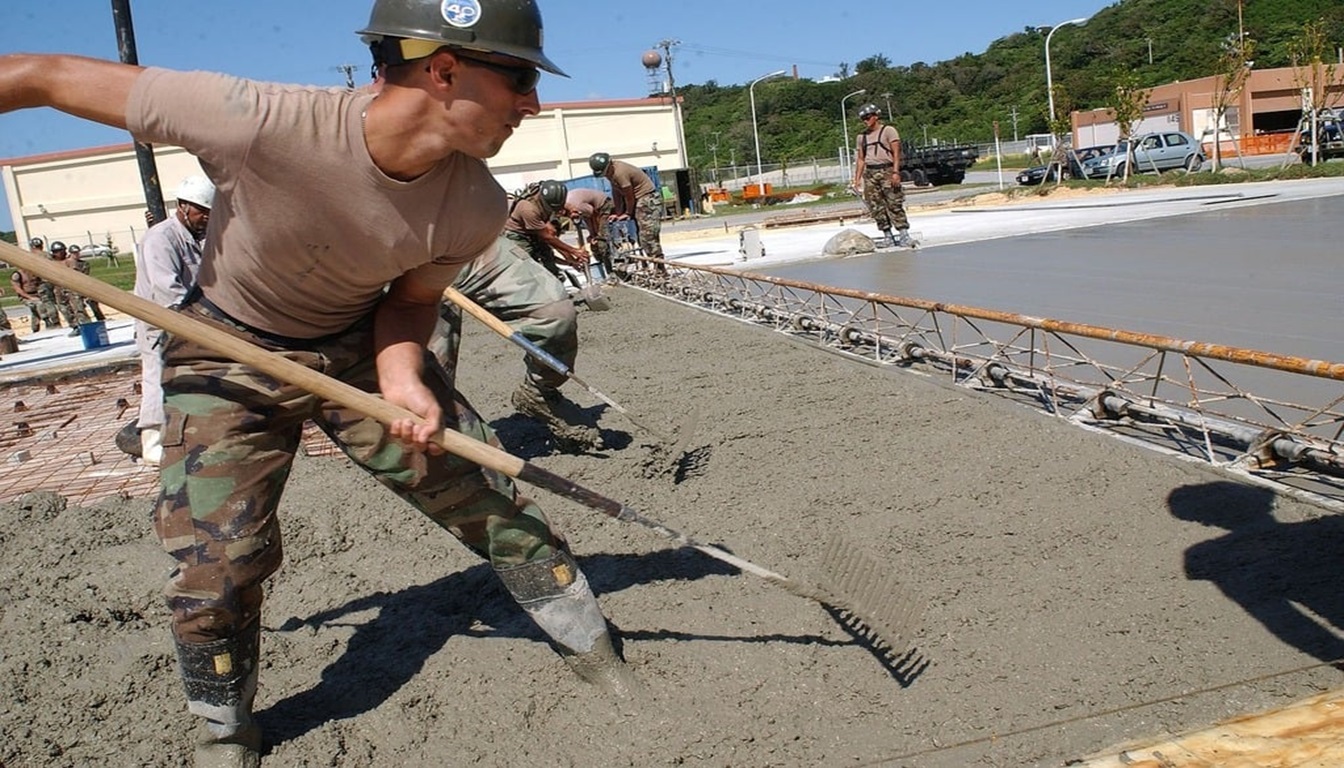
Placing and Consolidating
The 6th method is used in the concreting process placing and consolidating. Once the concrete is mixed, it needs to be placed into formwork or molds to take on the desired shape. Proper concrete placement is critical for achieving the desired strength and integrity of the finished structure.
During the process of concrete consolidating, the mixture is compressed and compacted to remove voids and ensure uniform density. Several methods can be used for consolidating concrete, including tamping, rodding, and vibration.


Vibrators, which are often used for larger projects, help to ensure proper concrete consolidation by vibrating the mixture and removing any excess air pockets. It is important to avoid over-consolidating the concrete, as this can cause segregation and weaken the overall structure.
Finishing
The last method used in the concreting process is finishing. After the concrete has been placed and consolidated, the surface can be finished to achieve the desired appearance and texture. Concrete finishing requires skill and expertise to ensure a high-quality finished product.
A variety of finishing techniques can be used, depending on the desired result. Some techniques create a smooth surface, while others add texture or patterns.
One common technique is floating, which involves using a handheld tool to smooth the surface of the concrete. Another technique is brooming, which creates a non-slip finish by pulling a broom across the surface while it is still wet.
Other finishing techniques include stamping, which imprints the surface with patterns or designs using special stamps, and polishing, which creates a glossy finish by grinding and polishing the surface.



Choosing the right finishing technique depends on the type of project, the desired aesthetic, and the intended use of the structure. Poorly executed finishing techniques can result in cracks, spalling, or other surface defects that can compromise the integrity and durability of the concrete.
Reinforcement
Concrete is a popular choice for construction due to its strength and durability. However, reinforcing materials such as steel bars or mesh are often added to further enhance these qualities. These materials are placed in strategic locations within the structure, creating a composite material that is highly resistant to both tension and compression.


The addition of reinforcement allows for the creation of structures that can withstand heavy loads and extreme weather conditions. It is commonly used in the construction of bridges, high-rise buildings, and other structures that require exceptional strength and durability.
Reinforcement can be added in a variety of forms, including pre-tensioned and post-tensioned reinforcement. Pre-tensioned reinforcement involves the use of steel cables that are tensioned before the pouring of the concrete. Post-tensioned reinforcement involves the use of steel cables that are tensioned after the concrete has been set.
Overall, the use of reinforcing materials is essential in creating long-lasting and strong concrete structures. It is crucial to ensure that the reinforcement is placed correctly and follows all building codes and regulations to ensure the safety and integrity of the structure.
Testing and Quality Control
Concrete testing and quality control are essential aspects of the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets the required standards of strength, durability, and safety. Testing and quality control procedures consist of a series of tests and inspections carried out at different stages of the concreting process.
The testing process involves measuring the properties of the concrete, such as its compressive strength, water-cement ratio, and workability. These tests are conducted both in the laboratory and on-site to ensure that the concrete meets the design specifications and can withstand the expected loads and environmental conditions.
Quality control measures involve monitoring the manufacturing process to prevent defects and ensure consistency in the quality of the final product. This includes checking the raw materials used, the accuracy of batching, mixing, and transportation methods, and the application of curing and finishing techniques.
Regular testing and quality control measures not only ensure that the concrete meets the desired standards but also help identify any potential issues that may arise during construction, such as cracks or uneven surfaces. By addressing these issues early on, the construction process can be more efficient and cost-effective in the long run.
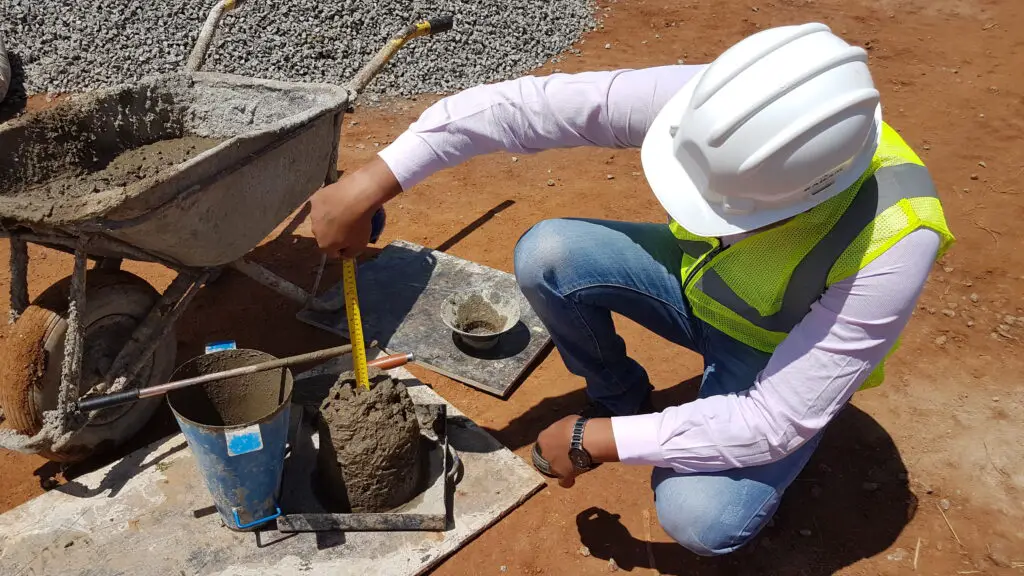


With concrete being a critical component of most construction projects, testing and quality control measures are vital to ensure the safety and longevity of the structures built. Regular inspection and testing can help identify potential problems early on and ensure that the final product meets the required standards of strength and durability.
Repair and Maintenance
Concrete structures are durable, but they are still susceptible to damage and deterioration over time. Regular concrete maintenance and repair procedures are crucial to ensuring the longevity and safety of these structures.
The first step to addressing any damage is to identify the cause and extent of the problem. Common issues include cracking, spalling, and corrosion of reinforcement materials. Once the cause and extent of the damage have been assessed, the appropriate repair method can be selected.
There are several techniques for concrete repair, including patching with cementitious materials, epoxy injection, and surface coatings. While patching is a common method, it may not be suitable for larger areas of damage. Epoxy injection can be used to fix cracks and other damage, while surface coatings can provide added protection and enhance the appearance of the structure.


Concrete maintenance is also essential to preventing damage and ensuring the longevity of the structure. Regular cleaning, sealing, and reapplication of coatings can help protect against weathering, abrasion, and chemical damage. Inspection and testing of the structure can also help identify potential problems before they become major issues.
Environmental Considerations
Concrete manufacturing has a significant impact on the environment due to its high carbon emissions. The production of Portland cement, the primary ingredient in concrete, accounts for up to 7% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
To mitigate these environmental issues and promote sustainable construction practices, the concrete industry has developed eco-friendly alternatives such as sustainable concrete. This concrete incorporates recycled materials, reduces the amount of Portland cement used, and adopts low-carbon production methods.
An example is pervious concrete, which allows water to pass through it, preventing stormwater runoff and replenishing groundwater supplies. Another is geopolymer concrete, which utilizes industrial waste materials such as fly ash to reduce the carbon footprint of the concrete manufacturing process.
“The development of sustainable concrete is a positive step toward reducing the environmental impact of the construction industry,” says John Smith, a construction expert at XYZ Corporation.
By adopting sustainable concrete practices, construction companies can minimize the concrete environmental impact and promote a more responsible approach to building.


Conclusion
In conclusion, the concreting process involves several steps that must be carried out meticulously to ensure the final product is strong, durable, and suitable for its intended use. From batching and mixing to transportation, compaction, curing, placing, consolidating, finishing, reinforcement, testing, and quality control, each stage requires attention to detail and adherence to industry standards. Additionally, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of concrete and explore sustainable practices to minimize its carbon footprint.
Overall, mastering the concreting process requires a combination of technical expertise, state-of-the-art equipment, and a commitment to quality and sustainability. By following these steps and incorporating best practices, the result is a strong and long-lasting concrete structure.
Thanks For the Great Attention!
Good Bye & Take Care
Happy Learning
Also, Read,
FAQ
What is concrete?
Concrete is a composite material made up of cement, water, aggregates (such as sand and gravel), and often additional additives. It is a versatile and widely used construction material due to its strength, durability, and ability to be molded into various shapes.
What are the different batching methods used in concrete manufacturing?
There are two main batching methods used in concrete manufacturing: volume batching and weight batching. Volume batching involves measuring the materials by volume, such as using buckets or containers. Weight batching, on the other hand, involves measuring the materials by weight using scales or weighing systems.



How is concrete mixed?
Concrete mixing involves combining the cement, water, aggregates, and any additional additives in a specific ratio to create a uniform mixture. This can be done manually using shovels or mechanically using specialized concrete mixers. The mixing process ensures that the ingredients are evenly distributed and well-blended.
What are the different methods of concrete transportation?
Concrete can be transported manually or mechanically. Manual transportation involves using buckets, wheelbarrows, or other containers to carry small quantities of concrete. Mechanical transportation, on the other hand, utilizes equipment such as trucks, conveyor belts, or pumps to transport large volumes of concrete efficiently and quickly.
Why is compaction important in concrete manufacturing?
Compaction is a crucial step in concrete manufacturing as it helps remove air voids, enhance the density of the concrete, and ensure proper bonding between the particles. Efficient compaction improves the strength, durability, and impermeability of the concrete, reducing the risk of cracking or structural damage.
What is the curing process in concrete manufacturing?
Curing is the process of maintaining the moisture and temperature conditions necessary for the concrete to gain strength and durability. It involves keeping the concrete damp or sealed for a specific period, typically a few days to several weeks, to allow the hydration process to occur and the concrete to harden properly.